Fair value gaps (FVGs) are powerful tools for understanding price movements in stocks and futures markets. These gaps occur when prices move rapidly, creating an imbalance that traders can use to their advantage. This guide provides an in-depth look at identifying, understanding, and trading FVGs to help you navigate the stock and futures markets with confidence.
Introduction to Fair Value Gaps
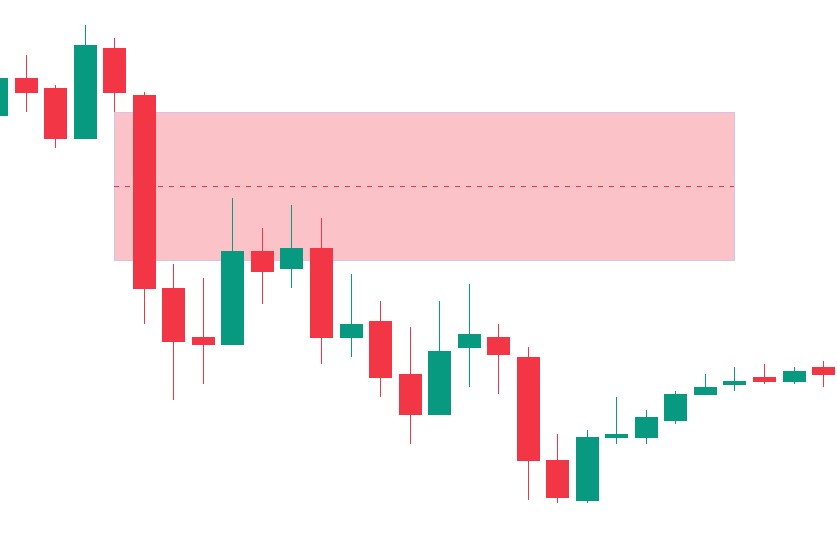
In stocks and futures markets, fair value gaps happen when there’s a noticeable price jump between the closing price of one session and the opening price of the next. These gaps often result from major market-moving news, including earnings announcements, economic data releases, or geopolitical events.
For traders, FVGs represent areas of price inefficiency that the market might revisit later. Recognizing these gaps can reveal potential entry and exit points, making them valuable tools for both day traders and long-term investors.
Identifying Fair Value Gaps
Spotting FVGs in stocks and futures markets involves a systematic approach:
- Candle Patterns on Charts: FVGs appear as gaps between the wicks or bodies of consecutive candlesticks. Use candlestick charts to easily find them.
- Analyzing Timeframes: Shorter timeframes (e.g., 5-minute charts) often reveal intraday gaps, while daily or weekly charts highlight larger, more impactful gaps.
- Event Monitoring: Keep an eye on earnings reports, Federal Reserve announcements, and geopolitical developments, as these often cause sharp price moves and FVGs.
Modern trading platforms offer tools to set alerts for significant price gaps, ensuring you don’t miss key opportunities.
Types of Fair Value Gaps
In the context of stocks and futures, FVGs generally fall into two categories:
- Bullish Gaps:
- Occur when prices gap upward, leaving untested levels below.
- Often show strong buying momentum in response to positive news or sentiment.
- These gaps can serve as support levels if prices retrace.
- Bearish Gaps:
- Happen when prices gap downward, leaving untested levels above.
- Usually show selling pressure due to negative news or market conditions.
- Such gaps can act as resistance if prices try to recover.
Understanding the type of gap helps align trading strategies with the market’s direction.
Trading Strategies for Fair Value Gaps
Trading FVGs in stocks and futures markets requires strategic planning. Here are some common approaches:
- Gap-Fill Strategy:
- Prices often “fill” FVGs by returning to the untested area. For example, if a stock gaps up, it might retrace to fill the gap before continuing higher. Traders can use this behavior to enter positions at favorable levels.
- Trend Continuation:
- When FVGs occur within a prevailing trend, they often signal that the trend will continue. For instance, a bullish gap in an uptrend could be a launchpad for further price increases.
- Reversal Opportunities:
- Large gaps sometimes show overreaction, making them prime spots for reversals. For example, a bearish gap due to panic selling might offer a buying opportunity once the market stabilizes.
Pair these strategies with proper risk management tools like stop-loss orders to protect your capital.
Case Studies and Examples
Let’s examine how FVGs play out in stocks and futures:
- Stock Market Example:
- A technology company announces record-breaking earnings after hours. The next day, the stock gaps up, leaving a fair value gap below. As the price consolidates, the gap serves as a support level, providing an excellent buying opportunity.
- Futures Market Example:
- A Federal Reserve interest rate decision causes S&P 500 futures to gap down overnight. The next day, the price retraces to partially fill the gap before resuming its downward trend, presenting a short-selling opportunity.
These examples highlight how FVGs can guide decision-making across different markets.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Trading FVGs can be rewarding, but traders often make these common mistakes:
- Ignoring Market Context:
- The Mistake: Treating all gaps the same, regardless of the broader market conditions.
- How to Avoid It: Always consider the news or events driving the gap. Is it earnings, a rate hike, or a one-off event? Use context to confirm the gap’s significance.
- Overtrading Gaps:
- The Mistake: Attempting to trade every gap without confirming its importance.
- How to Avoid It: Focus on high-probability gaps—those backed by strong technical or fundamental reasons. Avoid low-impact gaps that occur without significant volume or market activity.
- Neglecting Risk Management:
- The Mistake: Trading without stop-loss orders or risking too much capital on a single trade.
- How to Avoid It: Use a predefined risk management plan. Position sizes should align with your overall portfolio strategy, and stop-losses should be set just outside the gap area to manage potential losses.
- Failing to Backtest Strategies:
- The Mistake: Trading gaps without testing the approach on historical data.
- How to Avoid It: Use charting platforms to backtest gap strategies in different market conditions. This helps refine your approach before risking real money.
By addressing these pitfalls, traders can improve their consistency and reduce costly errors.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Fair value gaps offer a valuable lens into market dynamics in stocks and futures trading. They highlight areas of price inefficiency, providing opportunities for both intraday and swing traders. Here’s a summary of key takeaways:
- Understand the Basics: FVGs are price gaps that show potential trading opportunities.
- Use the Right Tools: Find gaps using candlestick charts and analyze them in the context of broader market trends.
- Adapt Your Strategy: Tailor your approach to the type of gap—bullish, bearish, or reversal opportunities.
- Avoid Common Mistakes: Stay disciplined, backtest strategies, and always manage your risk.
As you gain experience, FVGs can become a cornerstone of your trading strategy. For further learning, explore educational content, attend webinars, or use demo accounts to practice trading in real-market conditions.
Fair value gaps aren’t just technical patterns—they’re insights into how the market moves. Mastering them can give you a critical edge in the competitive world of stocks and futures trading.




Leave a comment